
- #Sudo apt get upgrade vs update install
- #Sudo apt get upgrade vs update update
- #Sudo apt get upgrade vs update software
#Sudo apt get upgrade vs update install
For example, to install GIMP image editor, you would run following commands − sudo apt-get updateĪPT-GET will download and install GIMP package, but it won't install any missing dependencies. Then, run "sudo apt-get install packagename" command to install package.
#Sudo apt get upgrade vs update update
First, run "sudo apt-get update" command to update list of available packages on your system. To install a package using APT-GET, you need to run two commands. For example, to install Chromium web browser, you would run following command − sudo apt install chromium-browserĪPT will automatically download and install any dependencies required for Chromium to run. To install a package using APT, simply run "sudo apt install packagename" command.
#Sudo apt get upgrade vs update software
Let's take a look at some examples of how you can use APT and APT-GET to manage software packages on your system. CompatibilityĪPT is more compatible with newer versions of Debian-based distributions, while APT-GET may be more compatible with older versions of these distributions. CommandsĪPT has a different set of commands than APT-GET, which can take some time to learn if you're used to using APT-GET. User InterfaceĪPT has a more user-friendly interface than APT-GET, making it easier for new users to manage software packages on their system. Here are some of most significant differences − Level of ControlĪPT-GET gives you more control over package management process, while APT is more automated and handles package dependencies for you. While APT and APT-GET are both package managers used on Debian-based Linux distributions, there are some key differences between two.
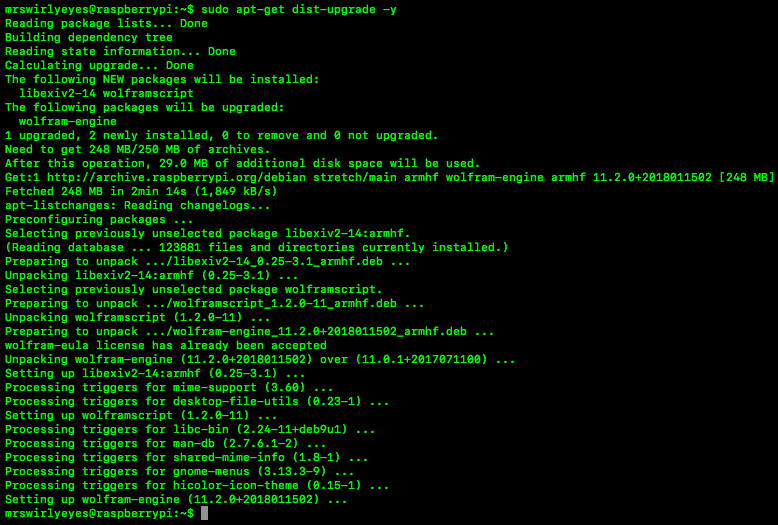
Instead, you need to use "sudo apt-get install -f" command to install any missing dependencies.ĪPT-GET can also be used to perform other package management tasks, such as updating your system, removing packages, and cleaning up package files that are no longer needed. However, it doesn't automatically install any dependencies that package requires. When you use APT-GET to install a package, it downloads package from a repository and installs it on your system. However, APT-GET is a more low-level tool that gives you more control over package management process. It's used to install, update, and remove packages from your system, much like APT. What is APT-GET?ĪPT-GET is a command-line tool that is part of APT package manager. This makes it easy to install software from different sources, and ensures that you have access to latest versions of software you need. A repository is a collection of software packages that are hosted online, and APT can be configured to use one or more repositories to install software on your system.
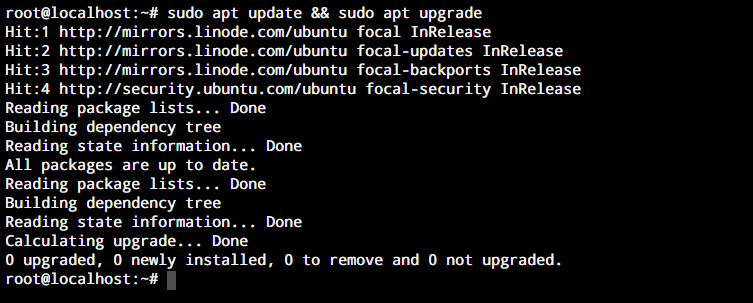
This ensures that all necessary dependencies are met, and that software runs smoothly on your system.Īnother advantage of APT is its ability to manage repositories. When you install a package using APT, it automatically installs any other packages that are required for that package to run. One of primary benefits of using APT is its ability to handle package dependencies. APT is built on top of a package management system called DPKG, which handles installation and removal of individual packages.
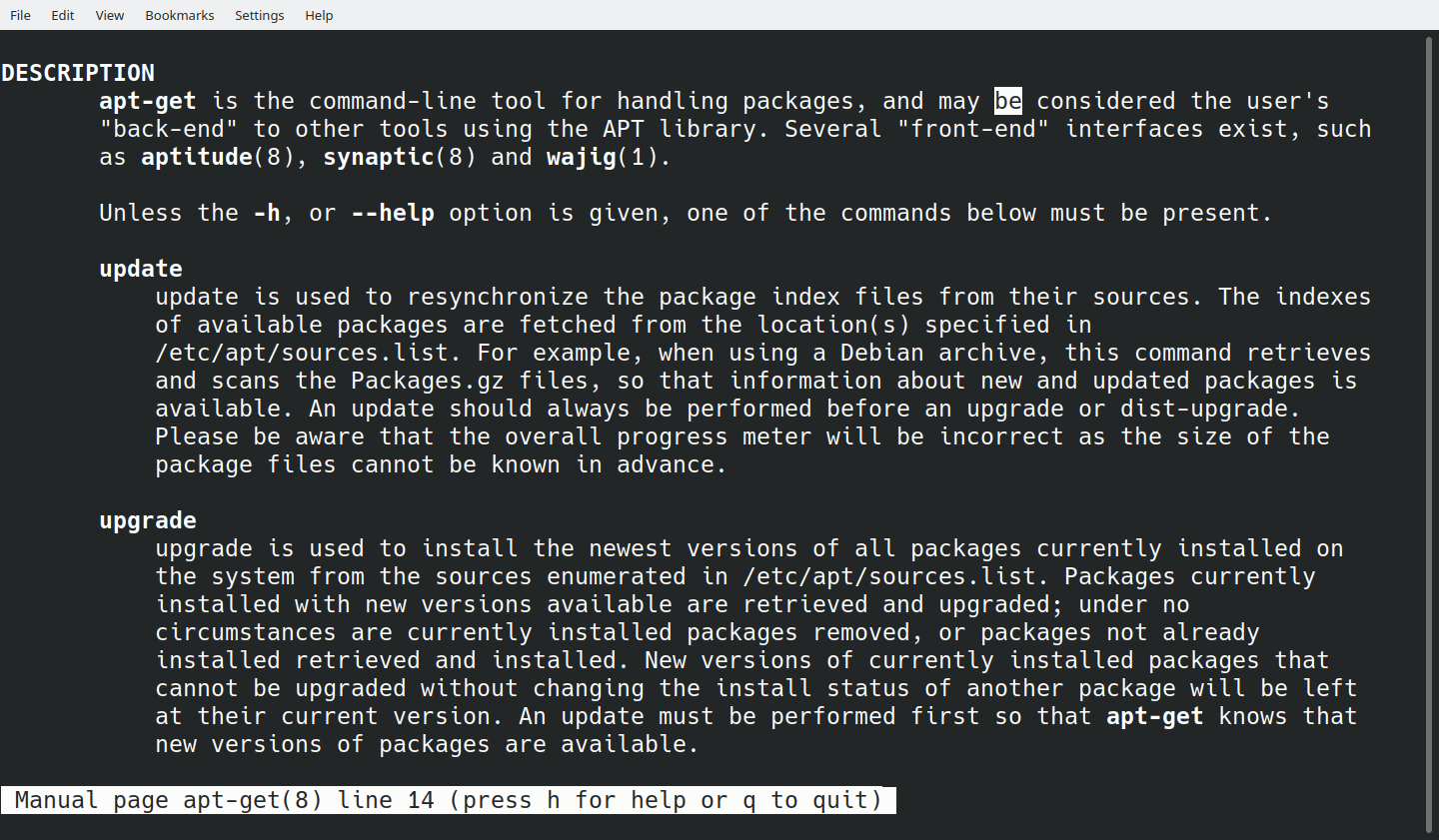
It's primary package manager used on Ubuntu, and it can be used to install, update, and remove software packages on your system. What is APT?ĪPT, short for Advanced Package Tool, is a command-line package manager used on Debian-based Linux distributions. In this article, we'll explore differences between APT and APT-GET, and how they affect way you manage software on your system. While both terms refer to package managers used to install and manage software on Debian-based Linux distributions like Ubuntu, they have some key differences. If you're a Linux user, you may have come across terms APT and APT-GET before.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
